Table of Contents
I'm writing this post as a follow-up of this article about HTTP Security Headers that I wrote a year ago to introduce a new kid on the block: its name is Expect-CT and - if you never heard about it - it's definitely worth a 5-min read.
In the first part of this post we'll mostly deal with the definition and learn the basics about the topic: then, we'll dig into the implementation part, explaining how to implement this new http security header on Apache, Nginx and IIS web servers.
Certificate Transparency
CT, as you might already know, is an acronym for Certificate Transparency, an open framework made by Google for monitoring and auditing the certificates issued by Certificate Authorities in near real-time. You can think of it as a open-data register that can (and most likely will) be used by all the CA to log all certificates they generate: by looking at that register, webmasters and site owners will be able to identify mis-issued certificates and protect their website - and their users - from forged certificates and/or rogue authorities.
If you want to know more about the framework, you can visit the Certificate Transparency official Website, where you'll find a lot of useful resources and infographics - including this awesome explanatory video:
The Expect-CT header
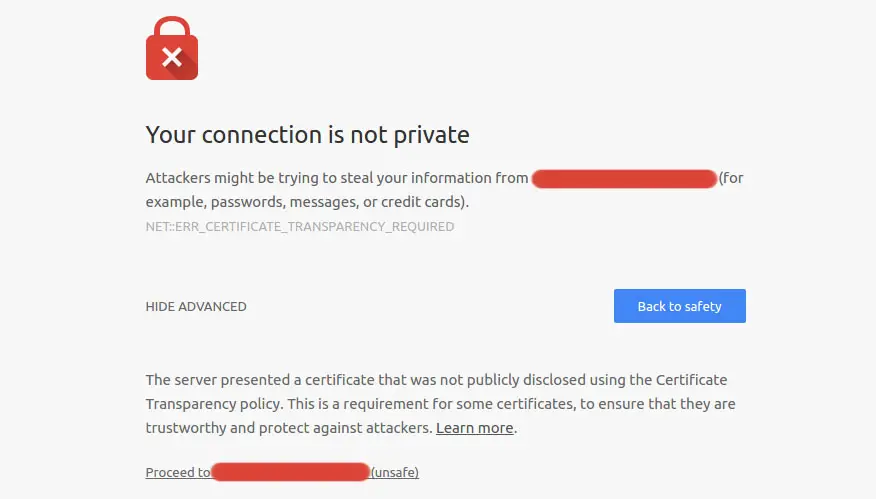
Now, let's see what does the Expect-CT header have to do with all that. Starting from July 2018 (Chrome 68), Google Chrome will not trust any SSL certificate that does not comply with the aforementioned Certificate Transparency Policy: that basically means that, if your certificate is not listed, your users and visitors will get the following security alert:
The Expect-CT header can be used to check that all your certificates have been properly listed: it can be implemented easily - very little configuration required - and can be added in two different operating modes: report-only (the default) and enforce. Here's the full set of available directives:
- enforce: the optional enforce directive controls whether the browser should enforce the policy or treat it as report-only mode. The directive has no value so you simply include it or not depending on whether or not you want the browser to enforce the policy or just report on it.
- max-age: the required max-age directive specifies the number of seconds that the browser should cache and apply the received policy for, whether enforced or report-only.
- report-uri: the absolute URL where the browser should send reports if it does not receive valid CT information.
Implementation examples
Here's a sample implementation of the report-only mode:
|
1 |
Expect-CT: max-age=0, report-uri="https://www.your-report-website.com/" |
By implementing this policy, whenever the browser doesn't find CT info regarding any certificate, it will send a report to the specified report-uri value (without terminating the connection): as we can see, we're using a max-age of 0 for this scenario - it's a report, therefore it makes little sense to cache it.
And here's a sample implementation for the enforce mode:
|
1 |
Expect-CT: enforce, max-age=300, report-uri="https://www.your-report-website.com/" |
With the following policy, the browser will now enforce the policy and cache it for 300 seconds - 5 minutes.
Apache
Here's how you can implement the Expect-CT http security header on Apache:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
<IfModule mod_headers.c> <Directory /> Header always set Expect-CT "enforce, max-age=300, report-uri='https://www.your-report-website.com/'" </Directory> </IfModule> |
If you want to implement the other security headers on Apache, check out this post.
Nginx
Here's how you can implement the Expect-CT http security header on Nginx:
|
1 |
add_header Expect-CT "enforce, max-age=300, report-uri='https://www.your-report-website.com/'"; |
If you want to implement the other security headers on Nginx, check out this post.
IIS
Here's how you can implement the Expect-CT http security header on Internet Information Services (IIS):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
<system.webServer> <httpProtocol> <customHeaders> <add name="Expect-CT" value="enforce, max-age=300, report-uri='https://www.your-report-website.com/'" /> </customHeaders> </httpProtocol> </system.webServer> |
If you want to implement the other security headers on IIS, check out this post.
Conclusions
That's about it: I sincerely hope that this post will help you to improve the security level of your web site(s)!
UPDATE: In case you're asking how to implement the report-uri endpoint for the Expect-CT header (and for other security headers as well), I strongly suggest to check out this post by shaun that illustrates how to do that with a simple PHP script.